REYKJAVIK–As a brown cloud of ash drifts down from the slopes of Eyjafjallajökull toward their truck, Hanna Kaasalainen warns a colleague that their gas masks won’t be much good against carbon dioxide. The masks filter out poisonous gases released by magma such as sulfur dioxide, but carbon dioxide can simply displace oxygen in the air, asphyxiating the researchers as they take ash samples alongside a haze-enshrouded, deserted road. “We shouldn’t stay very long,” the University of Iceland geochemistry graduate student advises, before strapping on a bright yellow mask and opening the door. Continue reading Iceland Eruptions Fuel Interest in Volcanic Gas Monitoring
Tag Archives: Planetary science
Haitians go home as government proposes relocation
Almost as soon as the earthquake hit Haiti on 12 January, urban planners and scientists dusted off plans to relocate some of Port-Au-Prince’s infrastructure away from the crowded city centre, which is dangerously close to the Enriquillo fault.
In discussions with the Haitian government last month, geophysicists advocated relocating critical city infrastructure to the north (See: Haiti earthquake may have primed nearby faults for failure, Nature News). Now, at a United Nations donors’ meeting today, Haitian officials are due to present their Action Plan for National Recovery and Development, which incorporates recommendations to rebuild some of Port-au-Prince’s infrastructure in provincial towns further from the fault (New York Times).
At the same time, some Haitians have begun returning to their homes, or at least the lots where their homes once stood, encouraged by relief agencies keen to avoid flooded refugee camps during the upcoming rainy season (Associated Press).
Read the rest of this blog post on The Great Beyond: [html] and see my previous article on the Haiti earthquake: [html]
Haiti earthquake may have primed nearby faults for failure
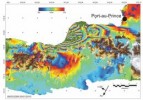 Geophysicists studying the 12 January earthquake in Haiti met yesterday with United Nations representatives and Haitian president René Garcia Préval to discuss what the latest measurements of the Earth’s shape can tell policymakers about future earthquakes. Several such ongoing geodesy studies suggest that the magnitude 7.0 earthquake, which has killed over 170,000 people so far, caused a 30- to 50-kilometre stretch of the fault southwest of Port-au-Prince to slip — possibly adding tension along an unreleased stretch of the same fault that passes even closer to Haiti’s capital.
Geophysicists studying the 12 January earthquake in Haiti met yesterday with United Nations representatives and Haitian president René Garcia Préval to discuss what the latest measurements of the Earth’s shape can tell policymakers about future earthquakes. Several such ongoing geodesy studies suggest that the magnitude 7.0 earthquake, which has killed over 170,000 people so far, caused a 30- to 50-kilometre stretch of the fault southwest of Port-au-Prince to slip — possibly adding tension along an unreleased stretch of the same fault that passes even closer to Haiti’s capital.
Read the rest of the story on Nature News [html] or here [pdf]
Apollo scientist dusts off ‘lost’ lunar data
 A new analysis based on an Apollo scientist’s copies of lost NASA data seeks to determine how sticky, abrasive moon dust will affect lengthier future lunar missions.
A new analysis based on an Apollo scientist’s copies of lost NASA data seeks to determine how sticky, abrasive moon dust will affect lengthier future lunar missions.
The author of the new study, Brian O’Brien, was the principal investigator for the dust detectors left behind in 1969 by the first two manned missions to the Moon, Apollo 11 and Apollo 12. At the time, O’Brien was a professor of space science at Rice University in Houston, Texas. Continue reading Apollo scientist dusts off ‘lost’ lunar data
